Forums
Welcome to the Internet frontpage discussion billboard, the best place to discuss topics with other users ranging from marketing, technology, health, beauty, entertainment etc.
Education vs Schooling: Understanding the Real Difference and Why It Matters
Discover the true difference between education and schooling — and why it matters. Learn how real education goes beyond classrooms, exams, and certificates to shape lifelong learning, personal growth, and global understanding.
Introduction
In everyday conversations, the words education and schooling are often used interchangeably.
Many assume they mean the same thing — after all, both involve learning, teachers, and knowledge. However, the truth is that education and schooling are not identical. While schooling refers to the structured, institutional process of acquiring knowledge, education is a far broader, lifelong experience that shapes how we think, act, and interact with the world.
Understanding the difference between the two isn’t just about semantics — it reshapes how we view personal growth, innovation, and the role of learning in society.
What Is Education?
Education is a lifelong process of learning and development. It extends beyond classrooms, curriculums, or exams. True education happens everywhere — through reading, experiences, conversations, observation, self-study, travel, and even failure.
It’s the holistic cultivation of knowledge, skills, values, attitudes, and critical thinking that help individuals navigate life meaningfully. Education empowers people to make informed decisions, think independently, and contribute productively to society.

What Is Schooling?
Schooling, on the other hand, refers to the formal, structured system of learning within institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities. It follows an organized curriculum designed to meet specific academic objectives, usually assessed through grades, exams, and certificates.
While schooling plays an essential role in society, it often focuses more on what to learn rather than how to think. In many systems, students are taught to memorize facts rather than develop problem-solving or creative thinking skills.

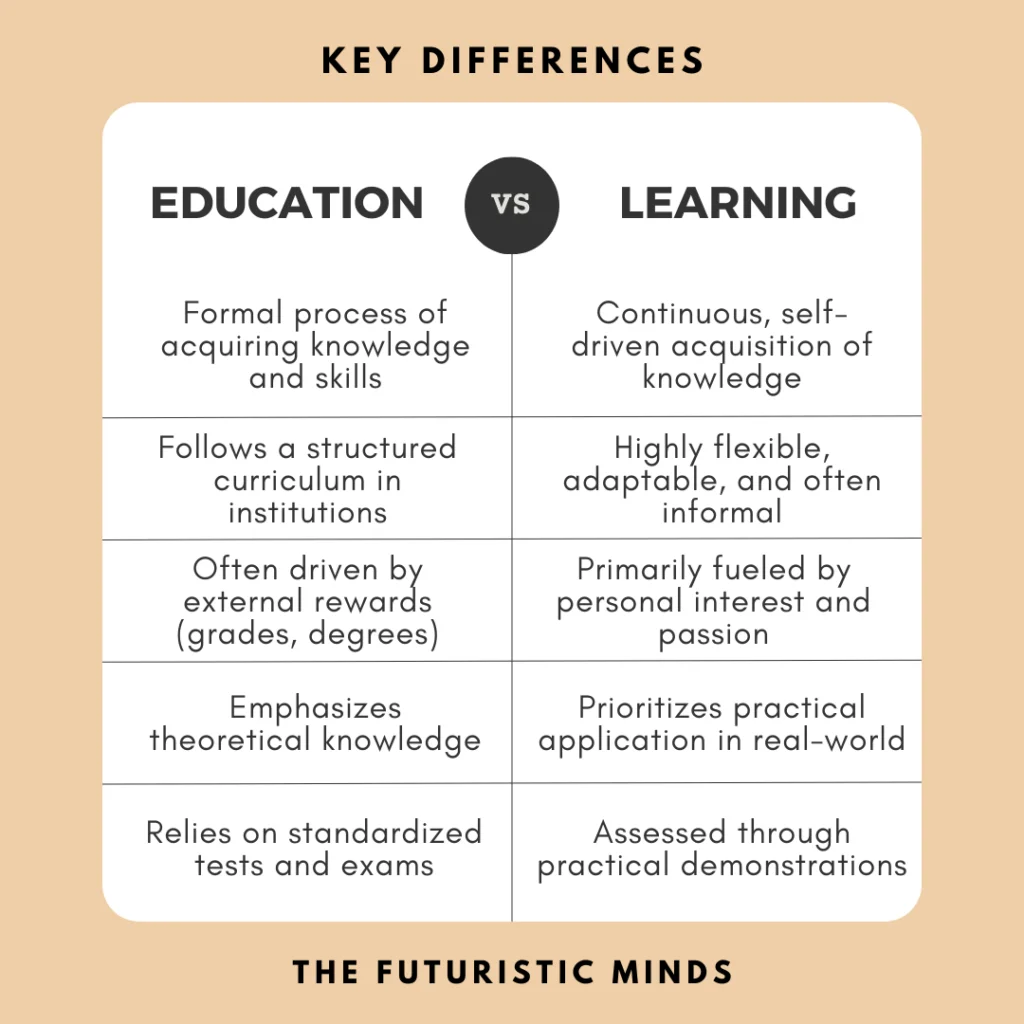
Key Differences Between Education and Schooling
| Aspect | Education | Schooling |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad and lifelong | Limited to formal academic environment |
| Learning Style | Flexible, self-driven, experiential | Structured, standardized, and institutional |
| Purpose | Personal growth, critical thinking, life skills | Academic achievement and certification |
| Setting | Anywhere — home, workplace, nature, online | Primarily in schools, colleges, and universities |
| Assessment | Based on real-life understanding and application | Based on tests, grades, and attendance |
| Creativity | Encourages independent thinking | Often limited by rigid curriculums |
| Duration | Lifelong | Time-bound (specific academic years) |
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Recognizing the distinction between education and schooling changes how we approach learning, teaching, and even parenting. When we equate education solely with schooling, we risk undervaluing informal and experiential learning — the kind that fuels innovation and personal transformation.
1. Education Builds Character; Schooling Builds Competence
Schooling equips us with technical skills, but education builds empathy, ethics, and emotional intelligence — traits essential for leadership and collaboration.
2. Education Promotes Lifelong Learning
True education doesn’t stop after graduation. It encourages curiosity, adaptability, and continuous self-improvement.
3. Education Prepares You for Life; Schooling Prepares You for Exams
While schooling measures success through grades, education measures it through understanding, impact, and growth.

The Interdependence Between Education and Schooling
Despite their differences, education and schooling complement each other. Effective schooling should nurture the spirit of true education — inspiring curiosity, creativity, and independent thought rather than rote memorization.
The best educational systems are those that balance academic structure with experiential learning, integrating real-world problem-solving into formal teaching.

Examples in Real Life
-
Self-Taught Innovators: Many successful entrepreneurs, inventors, and artists gained their skills through self-education rather than formal schooling — examples include Steve Jobs and Elon Musk.
-
Cultural Learning: Learning a new language or cultural custom outside school settings is education.
-
Online Learning Platforms: Today’s learners gain valuable skills from platforms like Coursera, YouTube, or Khan Academy — modern examples of education beyond schooling.
Modern Challenges
In today’s fast-changing world, schooling systems often lag behind technological and social advancements. Rigid curriculums, outdated teaching methods, and overemphasis on grades limit creativity and real understanding.
To thrive in the 21st century, individuals and institutions must shift from teaching to pass exams to learning to adapt, innovate, and lead.
How to Integrate Both Effectively
-
Encourage Curiosity Over Compliance
Teachers and parents should nurture curiosity and problem-solving rather than strict conformity. -
Promote Skill-Based and Experiential Learning
Combine theoretical lessons with practical experiences — internships, volunteering, and creative projects. -
Leverage Technology for Broader Education
Digital tools, online resources, and global collaboration make learning limitless. -
Redefine Success
Shift focus from certificates and grades to growth, competence, and emotional maturity.
Conclusion
Education and schooling are two sides of the same coin — but one side (education) gives the coin its real value. Schooling may end after graduation, but education never stops. It is the foundation for progress, empathy, and innovation across every generation.
By recognizing and embracing the true meaning of education, individuals and societies can move beyond rigid systems toward lifelong growth and global understanding.


