Cheapest Places to Live in the U.S.A (2026): Cities & States with the Lowest Cost of Living

Discover the cheapest places to live in the U.S. in 2026, including affordable cities and states with low housing costs, manageable expenses, and strong long-term livability.
Introduction
The cost of living in the United States varies dramatically from one region to another. While big metropolitan areas like New York and San Francisco command high prices for housing and daily expenses, many smaller cities and states offer exceptionally affordable living — sometimes up to 30% below the national average.
Affordability is influenced by factors such as job markets, housing costs, local taxes, and lifestyle options. Your ideal destination depends on what matters most: cost, career opportunities, quality of life, or community amenities.
What “Cheap to Live” Really Means
Before diving into specific places, it helps to understand what affordable living includes:
-
Housing costs: Rent or mortgage payments are usually the largest monthly expense.
-
Cost of living index: A weighted score that compares costs for goods, services, utilities, and housing against the U.S. average.
-
Income ratios: How much of local income goes toward shelter and essentials.
-
Employment and opportunities: Affordability is more meaningful when people can find jobs and sustainable income locally.
Cheapest Places to Live in the U.S. (2026): Cities With the Lowest Cost of Living
Finding a truly affordable place to live in the United States isn’t just about chasing the lowest rent. The cities that offer the best value combine reasonable housing costs, manageable daily expenses, access to jobs, and a livable quality of life. While large coastal metros continue to become more expensive, many mid-sized and smaller cities across the Midwest, South, and parts of the Northeast remain surprisingly affordable.
This section explores the cheapest cities to live in the U.S., based on a combination of housing affordability, cost-of-living indexes, income-to-expense balance, and long-term livability.
How These Cities Were Evaluated
Rather than relying on a single metric, affordability in this guide is based on a holistic approach, including:
-
Median home prices and average rent
-
Cost of living index compared to the U.S. average
-
Local wages relative to expenses
-
Utility, transportation, and grocery costs
-
Economic stability and access to essential services
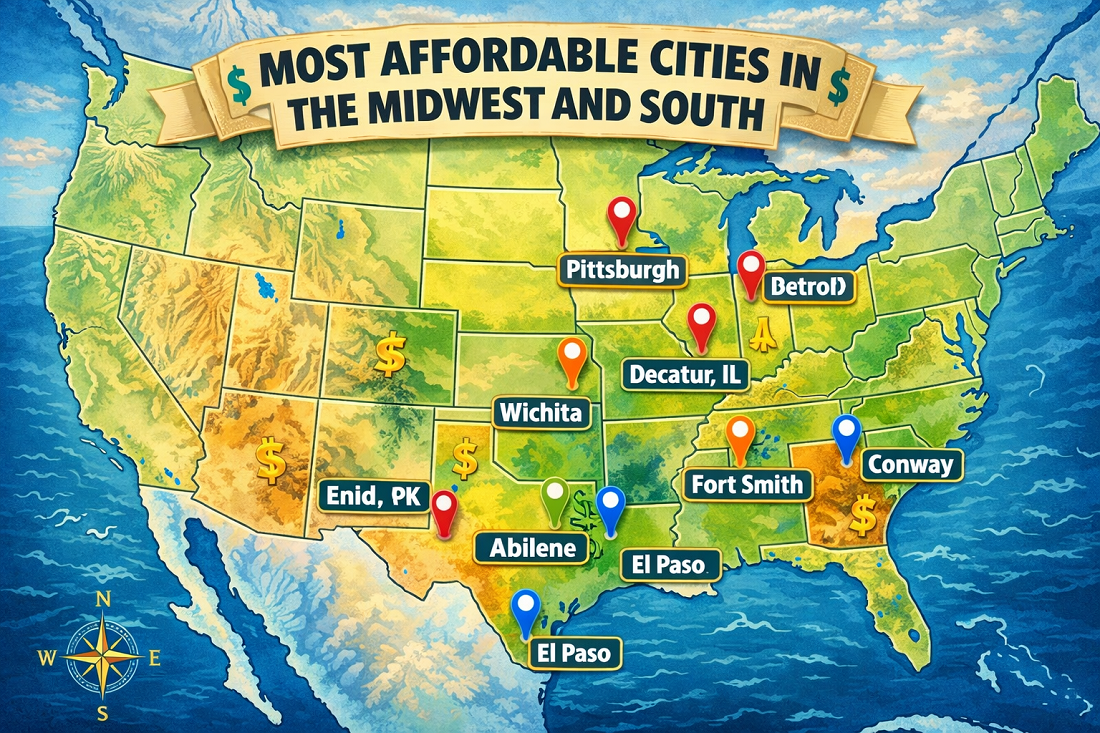
1. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh consistently ranks among the most affordable large cities in the country, especially when housing costs are weighed against income levels. Unlike many cities with rising rents, Pittsburgh’s housing market has remained relatively stable.
Median home prices remain far below those of comparable metro areas, while the city offers strong employment in healthcare, education, technology, and finance. Neighborhoods vary widely, allowing residents to choose between urban living or quieter residential communities without extreme cost differences.
Beyond affordability, Pittsburgh offers cultural amenities, major universities, and a strong sense of community, making it appealing to families, professionals, and retirees alike.

2. Decatur, Illinois
Decatur is often cited as one of the most affordable cities in the United States due to its exceptionally low housing prices. Both renters and homeowners benefit from costs that are significantly below the national average.
The city has a long manufacturing and agricultural history, and while it doesn’t offer big-city glamour, it provides stability, essential services, and a slower pace of life. Utility and grocery costs are also notably low, which helps reduce monthly expenses beyond housing.
Decatur is best suited for individuals or families prioritizing cost control over rapid career advancement in competitive industries.
3. Fort Smith, Arkansas
Fort Smith offers one of the best affordability-to-quality-of-life ratios in the South. Housing prices remain accessible, and rental rates are manageable even for single-income households.
The city benefits from a diversified local economy, including manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and retail. Transportation costs are low, traffic congestion is minimal, and many daily necessities are priced below national averages.
Fort Smith also appeals to those who value outdoor recreation, with nearby parks, trails, and natural scenery contributing to overall livability without added expense.

4. Wichita, Kansas
Wichita is one of the most underrated affordable cities in the U.S. Despite being Kansas’s largest city, it maintains housing costs far below those of similar metro areas.
The city is known for its strong aerospace and manufacturing industries, which provide relatively stable employment. Combined with low property taxes and reasonable utility costs, Wichita offers long-term affordability rather than just short-term savings.
Wichita also has a growing arts and food scene, contributing to a balanced lifestyle that doesn’t require a high income to enjoy.
5. Rockford, Illinois
Rockford’s affordability is driven largely by low housing prices and moderate living expenses. While the city has faced economic challenges in the past, revitalization efforts and infrastructure investments have improved livability in many areas.
For residents willing to research neighborhoods carefully, Rockford offers the opportunity to own property at a fraction of the cost found in major metropolitan regions. Utilities and transportation remain reasonably priced, helping keep monthly budgets manageable.
Rockford is often attractive to retirees, remote workers, and cost-conscious homeowners.

6. Enid, Oklahoma
Enid stands out for extremely low housing costs paired with a cost of living well below the national average. Renters, in particular, can find affordable options without sacrificing safety or access to basic services.
The city’s economy is supported by agriculture, energy, and nearby military installations, which contribute to economic consistency. Daily expenses such as groceries and utilities are also among the lowest in the country.
Enid is ideal for individuals who value financial simplicity and a quiet lifestyle over urban amenities.
7. Conway, Arkansas
Conway combines affordability with strong population growth, largely driven by education and healthcare sectors. Despite its growth, housing prices remain accessible compared to national benchmarks.
The city benefits from a youthful population, solid infrastructure, and relatively low transportation costs. Conway also maintains a cleaner, more modern feel than many similarly priced cities, which contributes to its rising popularity.
For families and professionals seeking affordability without stagnation, Conway presents a compelling option.

8. Abilene, Texas
Abilene offers affordable housing combined with the broader tax advantages of Texas. While wages may be lower than in major Texas metros, living costs are significantly reduced, allowing residents to stretch their income further.
The city has a strong military presence, healthcare employment, and education institutions, providing steady job opportunities. Property prices remain reasonable, and rental supply is relatively abundant.
Abilene is especially attractive to families and retirees who want affordability without state income tax burdens.
9. El Paso, Texas
El Paso is one of the most affordable large cities in the United States. Despite its size, housing costs remain surprisingly low, and the city consistently reports living expenses below the national average.
Utilities, groceries, and healthcare costs are also relatively affordable. El Paso’s border-city economy supports a wide range of industries, including trade, healthcare, education, and military employment.
For those seeking urban amenities without high urban costs, El Paso offers a rare balance.

10. Detroit, Michigan
Detroit’s affordability is largely driven by its low housing prices, particularly for buyers. While not every neighborhood offers the same experience, carefully chosen areas provide excellent value.
Ongoing redevelopment, infrastructure investment, and business growth have improved quality of life in many parts of the city. Utilities and transportation remain reasonably priced compared to coastal metros.
Detroit appeals to buyers and investors willing to do due diligence and focus on long-term potential.
Why These Cities Remain Affordable
Across these locations, several common patterns emerge:
-
Housing supply exceeds demand compared to major metros
-
Local economies are less speculative and more stable
-
Lower population pressure reduces rent inflation
-
Daily expenses remain below national benchmarks
These factors help maintain affordability even during periods of national housing market volatility.
Who These Cities Are Best For
Affordable cities like these tend to work best for:
Remote workers seeking lower expenses, Families prioritizing housing stability, Retirees on fixed incomes, First-time homebuyers, Individuals focused on saving or debt reduction
They may be less ideal for those seeking rapid career growth in niche industries concentrated in major metros.
Cheapest States to Live in the U.S. (2026): Where Overall Living Costs Stay Low
While individual cities can offer excellent affordability, many people prefer to evaluate cost of living at the state level. Statewide factors such as taxes, housing regulations, insurance costs, and utility pricing play a major role in determining how far your income will stretch over time.
The cheapest states to live in the U.S. tend to share common characteristics: lower housing demand, modest population growth, reasonable tax structures, and economies built around essential industries rather than speculative markets.
This section breaks down the most affordable states based on overall cost of living, not just home prices.
What Makes a State Affordable?
State-level affordability is influenced by a combination of long-term structural factors, including:
-
Median home prices and rental trends across the state
-
Utility and energy costs
-
Healthcare and insurance expenses
-
Transportation and infrastructure costs
-
Income-to-expense balance
Looking at states holistically avoids a common issue seen in many rankings, where a single cheap city masks higher costs elsewhere.

Mississippi
Mississippi consistently ranks as the lowest-cost state to live in the U.S. when measured by overall cost of living. Housing prices are among the lowest nationwide, and everyday expenses such as groceries, utilities, and transportation remain well below national averages.
Property prices are accessible across most of the state, not just in rural areas. While median incomes are lower than in high-cost states, the gap between income and expenses allows many residents to live comfortably without excessive financial strain.
Mississippi is best suited for individuals and families prioritizing affordability, stability, and homeownership over access to large metropolitan job markets.
West Virginia
West Virginia stands out for its exceptionally low housing costs and minimal population pressure. Median home prices remain among the lowest in the country, and rental markets are generally stable.
Utility costs are also relatively affordable, supported by local energy production. Transportation expenses tend to be manageable due to shorter commute distances and lower congestion compared to major metro states.
West Virginia appeals to retirees, remote workers, and those seeking lower living costs paired with a quieter lifestyle.

Oklahoma
Oklahoma offers a strong balance between affordability and economic opportunity. Housing prices remain accessible across most cities, and the cost of living stays below the national average.
The state benefits from diverse industries including energy, aviation, agriculture, healthcare, and logistics. Combined with reasonable utility costs and moderate taxes, Oklahoma offers long-term affordability rather than short-lived savings.
Oklahoma is often attractive to working professionals and families who want affordability without giving up job availability.
Missouri
Missouri’s affordability is driven by low housing prices, moderate property taxes, and reasonable insurance costs. Both urban and suburban areas remain accessible for buyers and renters alike.
The state’s central location also contributes to lower transportation and shipping-related costs, which helps keep consumer prices stable. Missouri offers a variety of lifestyle options, from small towns to major metro areas, without dramatic cost differences.
Missouri is a strong option for households seeking flexibility, affordability, and access to regional job hubs.
Arkansas
Arkansas consistently ranks among the most affordable states due to its low housing costs and inexpensive daily necessities. Utility prices are particularly favorable, helping reduce long-term household expenses.
The state’s economy is supported by agriculture, manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, providing steady employment opportunities without extreme competition. Housing affordability extends beyond rural areas into growing cities and suburbs.
Arkansas works well for families, retirees, and cost-conscious professionals seeking stability.

Indiana
Indiana remains one of the most affordable Midwestern states, offering low housing costs combined with relatively strong wages in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
Property prices are accessible throughout much of the state, and utility and transportation expenses remain manageable. Indiana’s central location also contributes to lower overall costs for goods and services.
The state appeals to first-time homebuyers and families looking for predictable expenses and economic stability.
Kentucky
Kentucky offers low housing costs, reasonable taxes, and moderate healthcare expenses. Much like Indiana and Missouri, affordability is spread across the state rather than concentrated in one or two cities.
Energy costs are generally below national averages, and transportation expenses remain low due to shorter commute distances. Kentucky’s cost structure supports long-term affordability rather than temporary market dips.
The state suits households looking for affordable living with access to both rural and urban environments.
Alabama
Alabama’s affordability comes from low housing prices, competitive utility costs, and modest property taxes. Many cities and towns across the state remain accessible for buyers and renters.
The state has a growing presence in manufacturing, aerospace, and healthcare, helping support employment without driving up housing demand excessively.
Alabama is attractive to families and retirees seeking affordability paired with economic consistency.

How Taxes Affect State Affordability
Taxes can significantly influence how affordable a state feels in practice:
-
States with lower property taxes reduce long-term housing costs
-
States without high income taxes can offset lower wages
-
Sales tax structures impact everyday expenses
Affordable states often maintain a balance where taxes do not overwhelm housing and income advantages.
Cheapest States vs. Highest Opportunity
It’s important to understand that the cheapest states are not always the highest-paying states. The best value often comes from places where:
Housing costs are low, Employment is stable (even if wages are moderate) and Daily expenses remain predictable.
For many households, this balance matters more than headline income numbers.
Who Should Consider These States?
Living in a low-cost state is especially beneficial for:
Remote workers earning out-of-state income, Retirees on fixed or investment income, Families seeking long-term housing stability, First-time buyers priced out of high-cost regions and Individuals focused on saving, investing, or debt reduction.
How to Choose the Right Affordable State for You
When narrowing your options, consider:
-
Job availability in your field
-
Climate and weather preferences
-
Healthcare access and quality
-
Long-term population and housing trends
Affordability works best when it aligns with lifestyle needs.
How to Choose the Cheapest Place to Live in the U.S. (Cities vs States)
Affordability isn’t a single number, and it isn’t static. Many people make costly mistakes by choosing a place that looks cheap on paper but becomes expensive over time due to hidden costs, weak job markets, or lifestyle mismatches.
The real challenge isn’t finding the cheapest place — it’s finding the place where your income, expenses, and lifestyle stay balanced year after year.
This section explains how to think clearly about affordability so your decision holds up long after the move.

City Affordability vs State Affordability: What’s the Difference?
Choosing an affordable city is often about precision. A single city can offer low housing costs, walkable neighborhoods, and access to jobs even if the rest of the state is more expensive. This approach works well for people who already know where they want to work or who rely on remote income.
Affordable states, on the other hand, offer broader financial stability. When an entire state has low housing costs, reasonable taxes, and manageable daily expenses, it reduces the risk of future cost spikes. If you plan to move again within the same state, buy property, or raise a family, statewide affordability matters more than a single cheap zip code.
The strongest long-term outcomes usually come from cities that sit inside already affordable states. That combination limits downside risk while preserving flexibility.
Why “Cheap” Sometimes Becomes Expensive Later
A lot of people and job portals usually rank places as cheap based on one snapshot in time. That approach ignores how quickly affordability can change.
Some cities appear cheap because wages are low, not because expenses are manageable. Others experience rapid population growth, which pushes rents and home prices up within a few years. In some cases, low housing prices are offset by higher transportation, healthcare, or insurance costs.
True affordability holds up when:
-
housing costs grow slowly
-
income opportunities are stable
-
essential services remain accessible
-
infrastructure can support growth
Places that fail on these points often feel cheap only at the beginning.

The Income-to-Expense Balance Matters More Than Price
A lower rent does not automatically mean a better financial outcome.
What matters more is how much of your income remains after covering essentials. Two people paying the same rent can experience very different affordability depending on taxes, utilities, healthcare, and commuting costs.
Cities and states that rank well long-term tend to keep this balance intact. Expenses stay predictable, and residents are not forced to spend a growing share of income just to maintain the same lifestyle.
This is why some moderately priced areas outperform extremely cheap ones when measured over a decade rather than a year.
Remote Work Has Changed the Affordability Equation
Remote work has quietly reshaped the map of affordable living.
People earning income tied to higher-cost regions can live comfortably in lower-cost cities and states without sacrificing earning potential. This allows households to prioritize housing stability, savings, and quality of life.
However, remote workers should still evaluate internet reliability, healthcare access, and local infrastructure. A place can be inexpensive and still fail to support modern work needs.
When remote income is stable, affordability becomes less about wages and more about expense control.

Lifestyle Costs People Often Overlook
Many affordability rankings ignore lifestyle-related expenses that quietly add up.
Transportation is a common example. A cheap house far from jobs, schools, or services can lead to higher fuel and maintenance costs. Healthcare access is another overlooked factor, especially for families and retirees. Insurance premiums and travel time can erase housing savings.
Climate also plays a role. Extreme heat or cold can raise utility bills significantly, changing the real cost of living over time.
The most affordable places tend to minimize these hidden costs rather than just advertising low housing prices.
Buying vs Renting in Low-Cost Areas
Low-cost cities and states often create opportunities for homeownership that are impossible in high-cost regions. Buying can lock in housing expenses and protect against rent inflation, but it only works if the local market is stable.
In areas with declining populations or weak job growth, extremely cheap homes may struggle to hold value. In contrast, moderately affordable markets with steady demand often provide better long-term outcomes.
Renting can be the smarter choice in cities where affordability is driven by short-term conditions rather than structural stability.

How to Know If a Place Will Stay Affordable
Affordability that lasts usually comes from slow, steady growth rather than sudden popularity.
Places that remain affordable over time tend to show:
-
gradual population growth
-
diversified local economies
-
consistent housing supply
-
infrastructure investment that keeps pace with demand
When affordability is driven by fundamentals rather than hype, it is more likely to endure.
Putting It All Together
The cheapest place to live is not the same for everyone.
For some, it’s a small city with extremely low housing costs. For others, it’s a state where expenses stay predictable even as income grows. The strongest decisions consider today’s costs and tomorrow’s stability at the same time.
By combining insights from affordable cities and affordable states, you gain the ability to choose a place that supports not just lower expenses, but a more sustainable financial life.
How to Move to a Cheaper Place Successfully (and Avoid Costly Mistakes)
Finding an affordable place to live is only half the equation. Many relocations fail not because the destination was wrong, but because the move was rushed, poorly evaluated, or based on incomplete assumptions.
This final section focuses on how to turn affordability research into a successful long-term move, while avoiding the traps that make “cheap” living unexpectedly expensive.

Why People Regret “Cheap” Moves
One of the most common mistakes people make is assuming that low housing costs guarantee an easier life. In reality, regret usually comes from discovering hidden expenses or lifestyle limitations after the move.
Some places feel affordable only because wages are low or opportunities are limited. Others require higher transportation spending due to long distances between work, schools, and services. In certain cases, healthcare access or insurance costs quietly erode monthly savings.
Affordability that works long-term always aligns with how you actually live, not just what you pay in rent or mortgage.
How to Compare Real Costs Before You Move
Before committing to a location, it’s important to simulate your real monthly life, not an idealized version.
Instead of focusing only on average rent or home prices, look at what your full budget would look like six months after settling in. That includes utilities based on climate, commuting habits, healthcare needs, groceries, and local taxes.
A useful approach is to compare your current monthly spending against realistic estimates in the new location. When the difference still favors the move after everything is included, affordability is likely genuine.
Renting First Is Often the Smartest Move
Even in very affordable cities and states, renting first provides valuable flexibility.
It allows you to test neighborhoods, commute patterns, and daily life without locking yourself into a long-term commitment. Many people discover that one part of a city fits their lifestyle far better than another, even if prices are similar.
Buying works best when affordability is supported by stable employment, population trends, and long-term housing demand. Rushing into ownership simply because prices are low can create challenges later.
Timing Matters More Than People Think
Moving costs fluctuate more than most people realize.
Housing markets have seasonal patterns, utility costs vary by time of year, and job availability can shift based on economic cycles. Moving during peak demand periods often reduces the savings that initially attracted you to a location.
Patience can turn a good affordability decision into a great one. Waiting for the right timing often improves both housing options and financial outcomes.
Don’t Ignore Long-Term Stability
Affordability should be sustainable, not temporary.
Cities and states that remain affordable over time usually show steady job growth, gradual population changes, and consistent infrastructure investment. Places that experience sudden booms often see rapid cost increases that erase early savings.
Looking at trends over the past decade often tells you more than any single ranking or headline.
When Cheap Living Works Best
Lower-cost cities and states tend to work especially well for people who value financial breathing room.
Remote workers often benefit the most, since their income is not tied to local wage levels. Retirees also gain stability when expenses remain predictable. Families benefit when housing costs leave room for education, healthcare, and savings.
The key is alignment. When affordability supports your goals rather than restricting them, the move succeeds.

A Simple Way to Make the Final Decision
When choosing between multiple affordable options, clarity usually comes from answering one question honestly:
Will this place still feel affordable after the excitement of moving fades?
If the answer is yes — based on expenses, opportunities, and lifestyle fit — then the decision is likely sound. If doubts remain about work, access, or long-term costs, it’s worth re-evaluating.
Affordability works best when it supports peace of mind, not constant trade-offs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the cheapest place to live in the United States right now?
There isn’t one single cheapest place for everyone. Affordability depends on housing costs, income opportunities, taxes, utilities, and lifestyle needs. Some smaller cities offer very low housing prices, while certain states remain affordable overall because daily expenses stay consistently low across regions.
The best option is usually a city located within a low-cost state, where both housing and long-term expenses remain manageable.
Are the cheapest places to live also good places to work?
Some are, and some aren’t. Many affordable cities have stable job markets in healthcare, manufacturing, education, logistics, and public services. However, wages can be lower in certain areas, which is why affordability should always be evaluated using income-to-expense balance rather than rent alone.
Remote workers often benefit the most from low-cost locations because their income is not tied to local wage levels.
Is it better to rent or buy in a low-cost area?
That depends on how stable the local housing market is and how long you plan to stay. Renting first is often a smart move when relocating, as it allows time to understand neighborhoods, job access, and daily expenses.
Buying tends to make sense in areas with steady population trends and long-term housing demand, where affordability is supported by fundamentals rather than temporary conditions.
Why are some cities so much cheaper than others?
Cities remain affordable for different reasons. Some have slower population growth, lower land demand, or economies built around essential industries rather than speculative markets. Others benefit from lower taxes, reduced congestion, or lower construction costs.
Affordability usually lasts longer in places where growth is gradual rather than driven by sudden popularity.
Do low-cost states have higher taxes or hidden costs?
Not necessarily. Some affordable states have lower housing costs but moderate taxes, while others balance taxes with low utility, insurance, and transportation expenses. The key is to look at total monthly living costs rather than focusing on a single factor like rent or income tax alone.
Hidden costs often come from transportation, healthcare access, or climate-related utility expenses rather than taxes themselves.
Can affordable places become expensive over time?
Yes. Affordability can change as cities grow, attract new residents, or experience housing shortages. That’s why it’s important to look at long-term trends, not just current prices.
Places that remain affordable usually show steady growth, diversified economies, and enough housing supply to meet demand.
Are affordable places suitable for families?
Many low-cost cities and states are family-friendly, especially where housing stability allows families to plan long term. Factors such as school quality, healthcare access, safety, and infrastructure matter just as much as cost when choosing a place to raise a family.
Affordability works best when it supports daily life, not when it creates trade-offs that affect quality of living.
How should I compare two affordable locations?
The most effective approach is to compare full monthly expenses rather than individual costs. That includes housing, utilities, transportation, groceries, healthcare, and taxes.
When a location remains affordable even after accounting for all these factors, it is more likely to provide long-term financial comfort.
Final Note - Thoughts & Next Steps
The cheapest places to live in the U.S. are not defined by one city or one state. They are defined by balance.
When housing costs, daily expenses, income opportunities, and lifestyle needs align, affordability becomes sustainable. By combining city-level precision with state-level stability, and by planning moves thoughtfully, it’s possible to reduce living costs without sacrificing quality of life.
That’s the difference between simply moving somewhere cheap — and building a life that stays affordable.
If you found this guide helpful and want more well-researched, practical insights on living smarter, saving better, and making informed life decisions, you can sign up at novasvet.com to stay updated with new guides and resources.
If you have experience living in an affordable city or state — or you’re considering a move — feel free to share your thoughts or questions in the comments. Real-world experiences often add valuable perspective for others exploring similar decisions.
Your input helps keep this discussion useful, accurate, and grounded in real life.
- cheapest_places_to_live_in_the_us
- lowest_cost_of_living_states
- affordable_cities_in_the_united_states
- cheap_places_to_live_in_america
- cost_of_living_by_state_usa
- cheapest_cities_in_the_us
- affordable_places_to_live_in_the_us
- low_cost_of_living_areas_usa
- cheapest_states_to_live_in_2026
- cost_of_living_comparison_usa
- best_affordable_cities_in_america
- low_cost_housing_states_usa
- Science & Technology
- Education & Scholarships
- Health and Wellness
- Internet business
- Entertainment
- Government and Politics
- Weird & Mysterious
- Other