How to Build an AI Chatbot: Complete Blueprint Step-by-Step Guide for Businesses & Developers (2025)

Learn how to build a powerful AI chatbot from scratch or using existing frameworks. This comprehensive, Novasvet guide covers planning, AI models, NLP, tools, integrations, conversation design, training data, memory architecture, security, deployment, analytics, and real-world best practices.
Introduction
Chatbots and AI assistants have rapidly evolved from simple automated responders into intelligent conversational systems that can reason, remember, and interact almost like humans. Today, they support customer interactions, streamline business operations, assist with learning, automate repetitive tasks, and enhance user experience across digital platforms. Whether you’re a developer, a business owner, or just curious about the technology, understanding how modern chatbots are built — and what makes them effective — has become increasingly valuable.
In this comprehensive guide, we’re going to take you step-by-step through the full process of creating a chatbot, from foundational concepts to advanced real-world implementation techniques. You’ll not only learn what chatbots are and how they work, but also how to design their personality, structure their conversations, integrate them into systems, give them memory, connect them with data sources, keep them secure, and continuously improve them after deployment.
Unlike many articles that provide surface-level summaries, this one dives deeply into the real architecture, logic, decision-flow, and engineering principles behind powerful AI-driven chatbots. By the end, you’ll have a clear, practical understanding of how to build a chatbot that is truly useful — one that communicates naturally, understands the user’s intent, learns over time, and works reliably in real-world environments.
How to Build an AI Chatbot (Complete Step-by-Step Guide for 2025)
Artificial intelligence chatbots are transforming business, development, and digital interaction. But there’s a huge gap:
❗ Most guides only cover surface-level basics
❗ Most “tutorials” ignore real-world deployment
❗ Many focus strictly on either business or technical — not both
This article solves all of that.
You’re about to read the most complete, detailed, practical guide on building a chatbot. Whether you’re:
-
a developer building from scratch
-
a business owner wanting a bot for customer service
-
a startup building an AI product
-
a marketer automating user interaction
-
or an enthusiast experimenting with LLMs
You will walk away with clarity and a blueprint.
1 — Understanding What a Chatbot Actually Is
Most explanations are oversimplified:
“A chatbot is a computer program that talks to humans.”
But let’s define it properly.
A chatbot is a system that:
-
receives input (text / voice / context / data)
-
interprets user intent
-
retrieves or generates responses
-
may perform actions or automation
-
returns the best possible reply or result
There are 3 core types of chatbots:
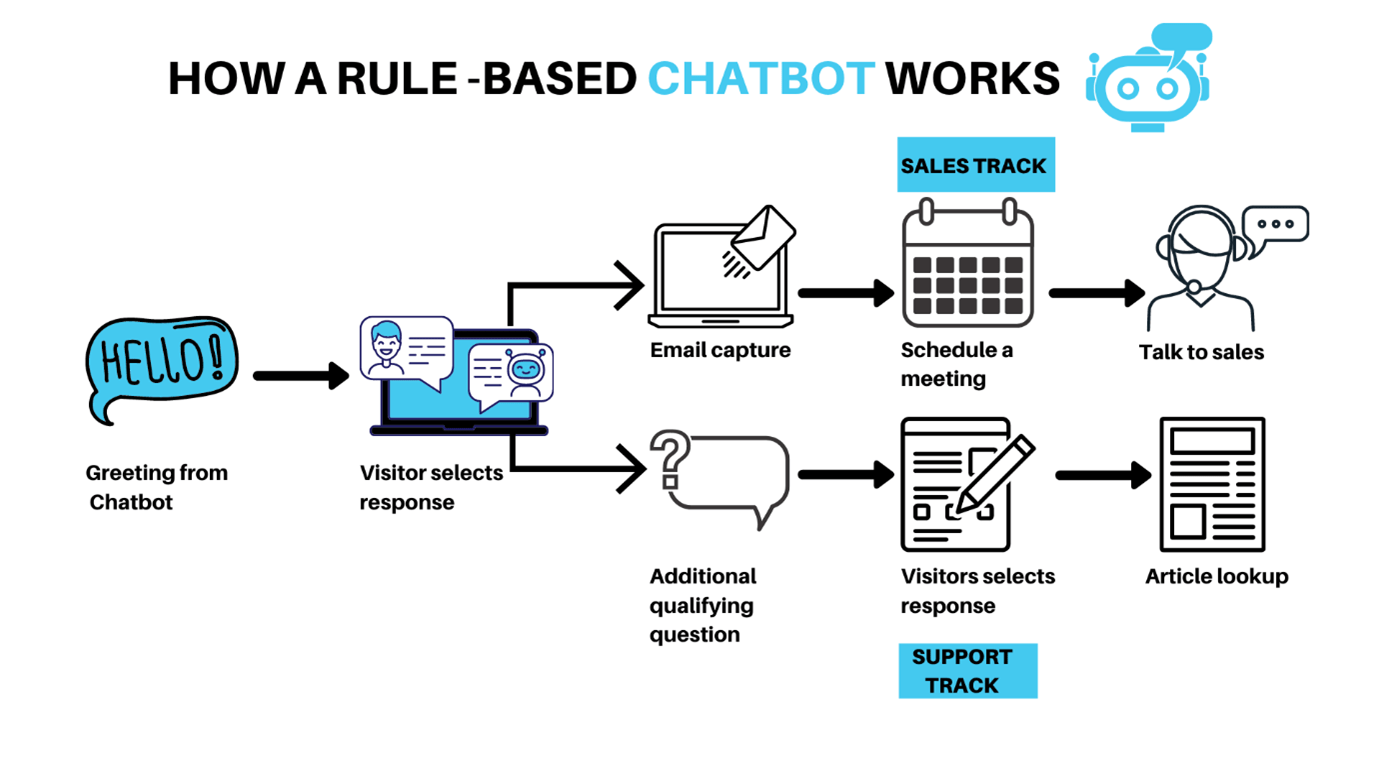
1. Rule-based chatbots
-
respond using pre-set responses
-
work with menu flows
-
predictable but limited
2. Retrieval-based chatbots
-
select responses from a knowledge base
-
use NLP to find the best matching answer
-
safer and predictable
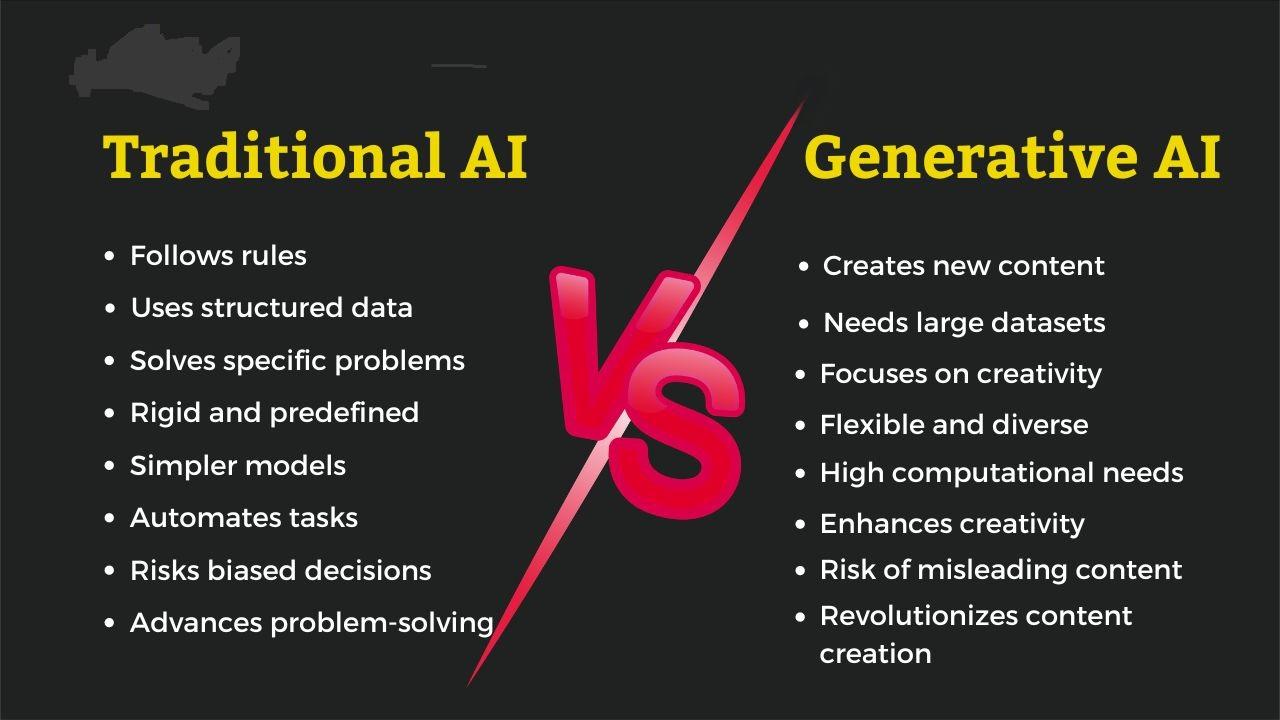
3. Generative AI chatbots (like GPT-based)
-
use large language models (LLMs)
-
generate responses dynamically
-
conversational and human-like
-
can reason, infer, relate context
2 — Define Your Chatbot’s Purpose (Business + Technical Alignment)
Most people immediately jump into coding.
That’s a mistake.
Ask the foundational question:
“What do I want this chatbot to do?”
Here are strategic categories:
A. Customer Support Bot
-
replies to FAQs
-
returns store info
-
tracks orders
-
handles complaints
-
support ticket escalation
B. Lead Generation / Sales Bot
-
qualifies leads
-
offers product recommendations
-
pushes users toward conversion
-
provides human handoff
C. Internal Business Bot
-
HR assistant
-
IT helpdesk
-
knowledge base navigation
-
training assistant
D. Developer-Focused Utility Bot
-
CLI assistants
-
debugging helper
-
engineering documentation navigation
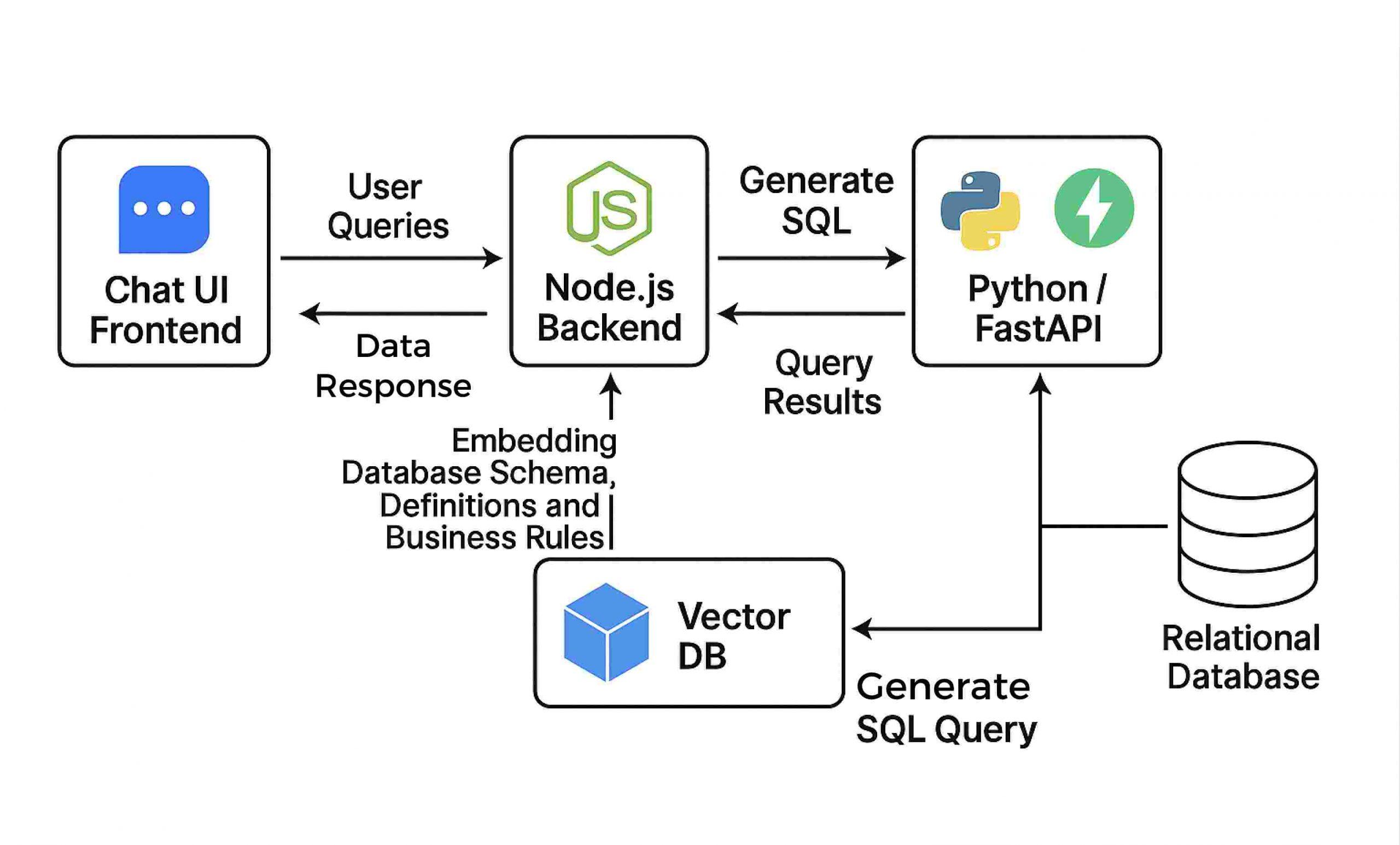
3 — Architecting the Chatbot: System Blueprint
Here’s the real architecture that most guides never explain.
Core components of a modern AI chatbot
-
Input interface
-
web chat widget
-
WhatsApp
-
Slack
-
Voice input
-
API endpoint
-
-
NLU / NLP processing (intent detection)
-
entity extraction
-
intent matching
-
-
Model layer
-
rule-based scripting
-
classification
-
retrieval
-
LLM (GPT-like generative model)
-
-
Memory & context storage
-
short-term conversation context
-
long-term user profile
-
embeddings in vector DB
-
-
Knowledge base
-
FAQs
-
docs
-
imported PDFs
-
corporate data
-
-
Action execution
-
call API
-
retrieve database records
-
trigger automation
-
-
Output generation
-
final response
-
suggested follow-up
-
call-to-action
-
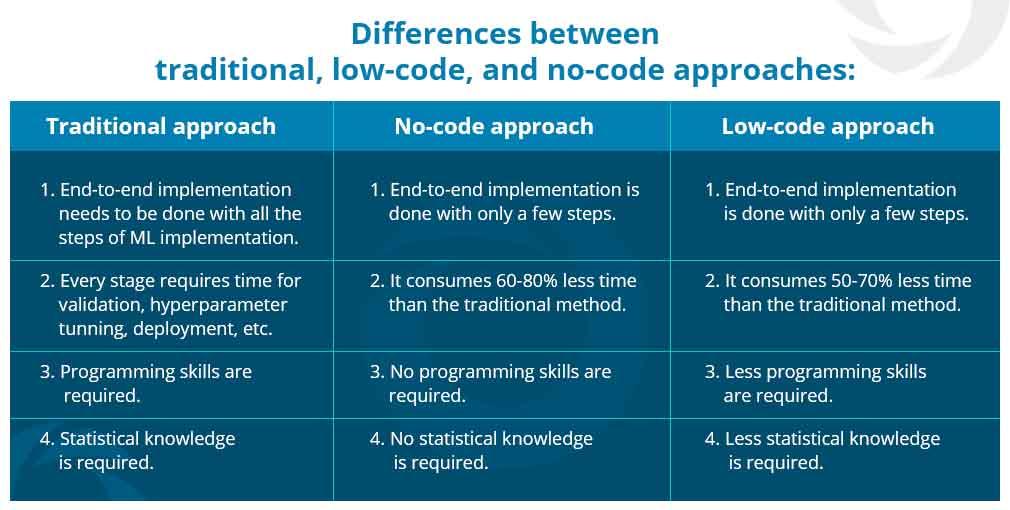
4 — Choosing the Right Approach: No-Code vs Low-Code vs Full Development
This section addresses both business and development needs.
1. No-Code Chatbot Builders (Fastest to launch)
Examples:
-
Tidio
-
Chatbot.com
-
Voiceflow
-
Make.com
Good for:
-
non-technical founders
-
simple chatbots
-
quick deployment
-
customer automation
Not good for:
-
deep customization
-
proprietary datasets
-
complex logic
-
custom memory systems
-
custom actions
2. Low-Code Approach
Examples:
-
n8n
-
Botpress
-
Retool
Good for:
-
moderate complexity
-
building prototypes
-
API integration
3. Full Custom Development (from scratch)
Languages / frameworks:
-
Python
-
JavaScript / Node.js
-
Next.js
-
Flask
-
LangChain
-
Rasa
-
spaCy
Good for:
-
enterprise-grade bots
-
confidential data control
-
full logic definition
-
ML training pipeline
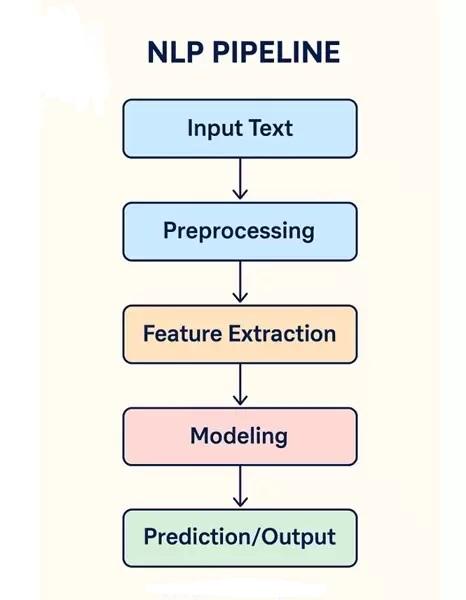
5 — How Chatbots Understand Users: NLP & Intent Recognition (Clear Explanation)
Even business readers will understand this.
User says:
“Where is my order?”
The chatbot must figure out:
-
user intent: order tracking
-
required entity: order number
-
user status: logged in / not logged in
How intent recognition works (simple explanation):
-
Convert user text into tokens
-
Compare embeddings with stored intent vectors
-
Select intent with highest semantic match
This is how AI knows that:
“track my package” ≈ “where is my order” ≈ “delivery status”
Even if the words differ.
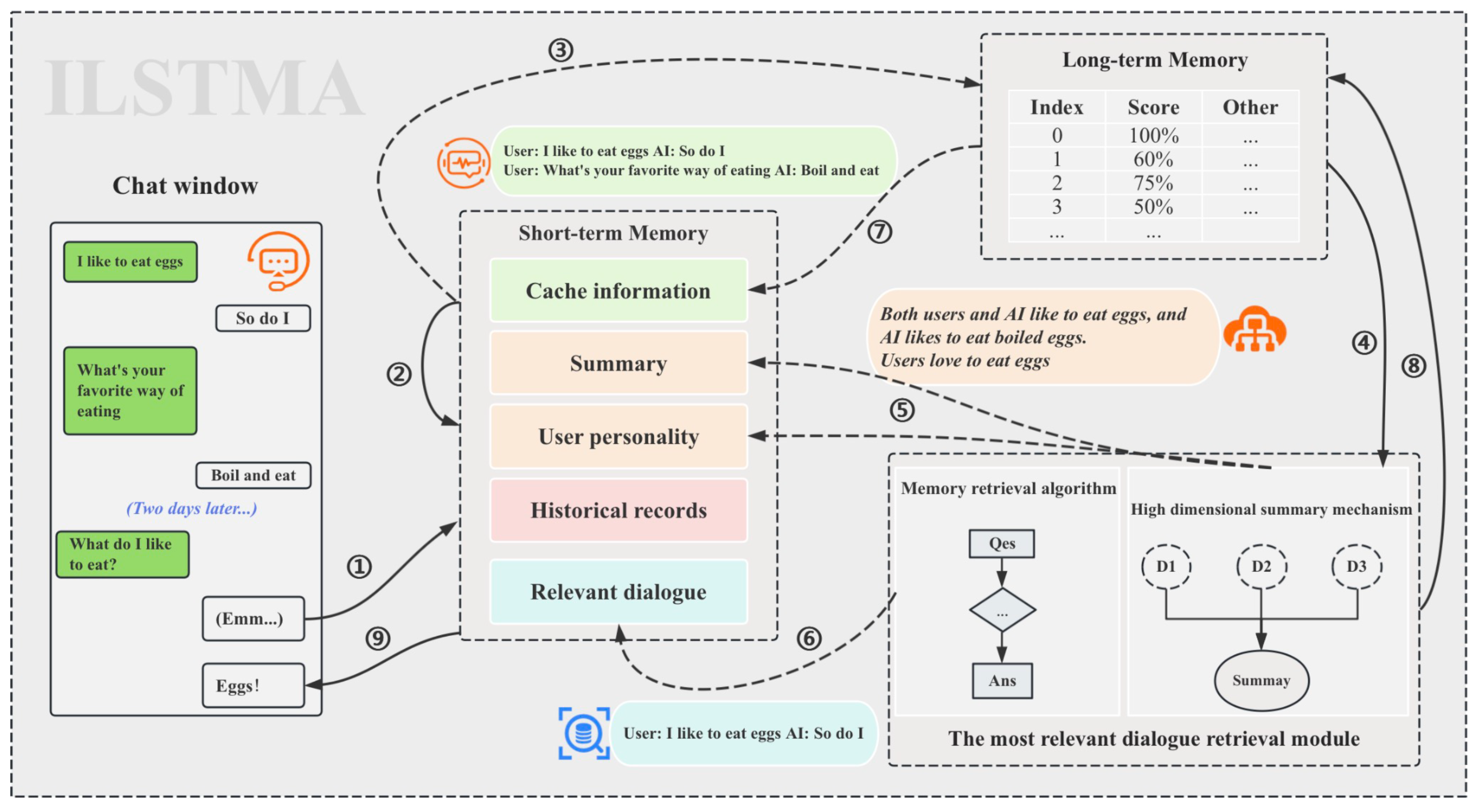
6 — Chatbot Memory: Short-Term vs Long-Term
To make a bot truly intelligent, it needs memory.
Short-term conversational memory
The chatbot remembers:
-
previous messages in the conversation
-
name of the user
-
current topic context
Example:
User: “My name is Kelvin.”
Later…
Bot: “Kelvin, I’ve found the information.”
Long-term memory
Stored in:
-
embeddings store
-
knowledge graph
Bot remembers over time:
-
preferences
-
purchase history
-
previous complaints
-
FAQs already answered
7 — Designing the Chatbot’s Personality & Communication Style
Even highly technical bots need personality guidelines.
A general AI assistant should be:
-
friendly
-
knowledgeable
-
concise
-
polite
-
context-aware
-
confidence-rated (knows when to admit uncertainty)
We define a personality script:
Tone: helpful, warm, intelligent
Formality: neutral–friendly
Reply length: short to medium unless asked for detail
Use of emojis: optional, minimal in professional contexts
Expression style: explains concepts as if teaching
Humility rule: if uncertain → ask clarifying questions
Example directive:
If you are not fully certain about a fact, ask a follow-up question instead of guessing.
This avoids hallucinations.
8 — Creating the Intent & User Journey Map
This is the real art of chatbot design.
Instead of random responses, we define structured communication flows.
Example intent categories for a general AI assistant:
-
Define a concept
-
Summarize text
-
Explain something step by step
-
Translate
-
Suggest actions
-
Recommend tools
-
Perform calculation
-
Brainstorm ideas
-
Retrieve knowledge
-
Ask clarifying questions
9 — Building & Preparing Training Data
Training data quality = chatbot intelligence.
Data sources may include:
-
FAQs
-
wiki pages
-
product documentation
-
website pages
-
manuals
-
tutorials
-
past support records
For a general AI assistant, we create:
Examples dataset
User: “explain machine learning”
Bot: “Machine learning is a type of AI where systems learn from data rather than explicit programming…”
User: “rewrite this in simpler English…”
Bot: “Sure, here’s a simplified version…”
User: “what does this code do?”
Bot: “This function takes X as input and returns Y…”
Negative training:
We also define what it should NOT do:
-
no fake info
-
no toxic language
-
no personal attacks
-
no copyright violation output
-
no medical/legal/financial guaranteed claims
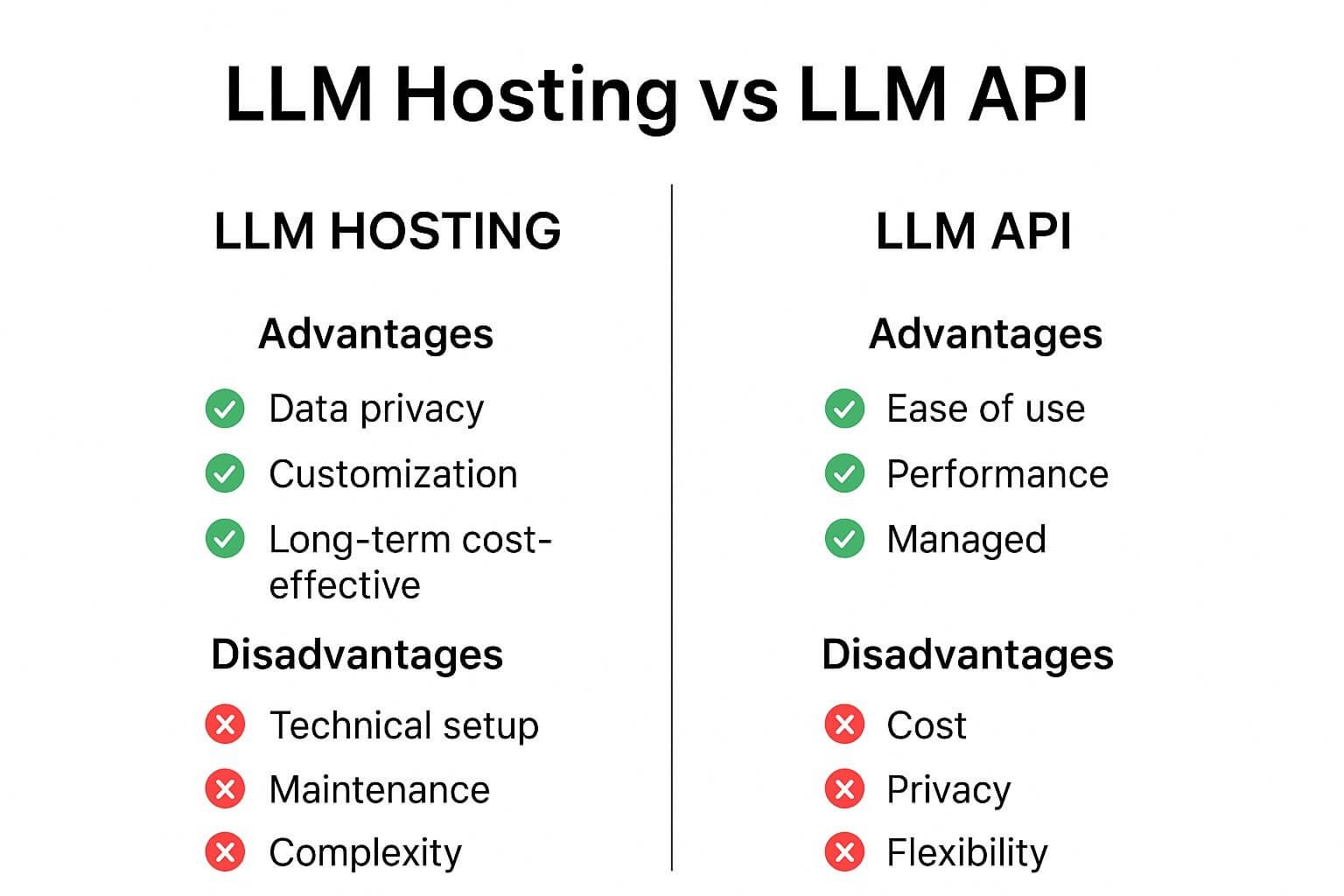
10 — Technical Model Layer: Which AI Model to Use
There are several choices:
Option A: Use existing LLM APIs
-
Claude
-
Llama APIs
-
DeepSeek
-
Mistral
Pros:
-
fastest
-
low cost
-
minimal engineering
-
strong performance
Cons:
-
data may leave your system
-
dependency on vendor
Option B: Self-host open-source models
Pros:
-
full control
-
local execution
-
privacy
-
no vendor lock-in
Cons:
-
requires GPUs
-
requires tuning
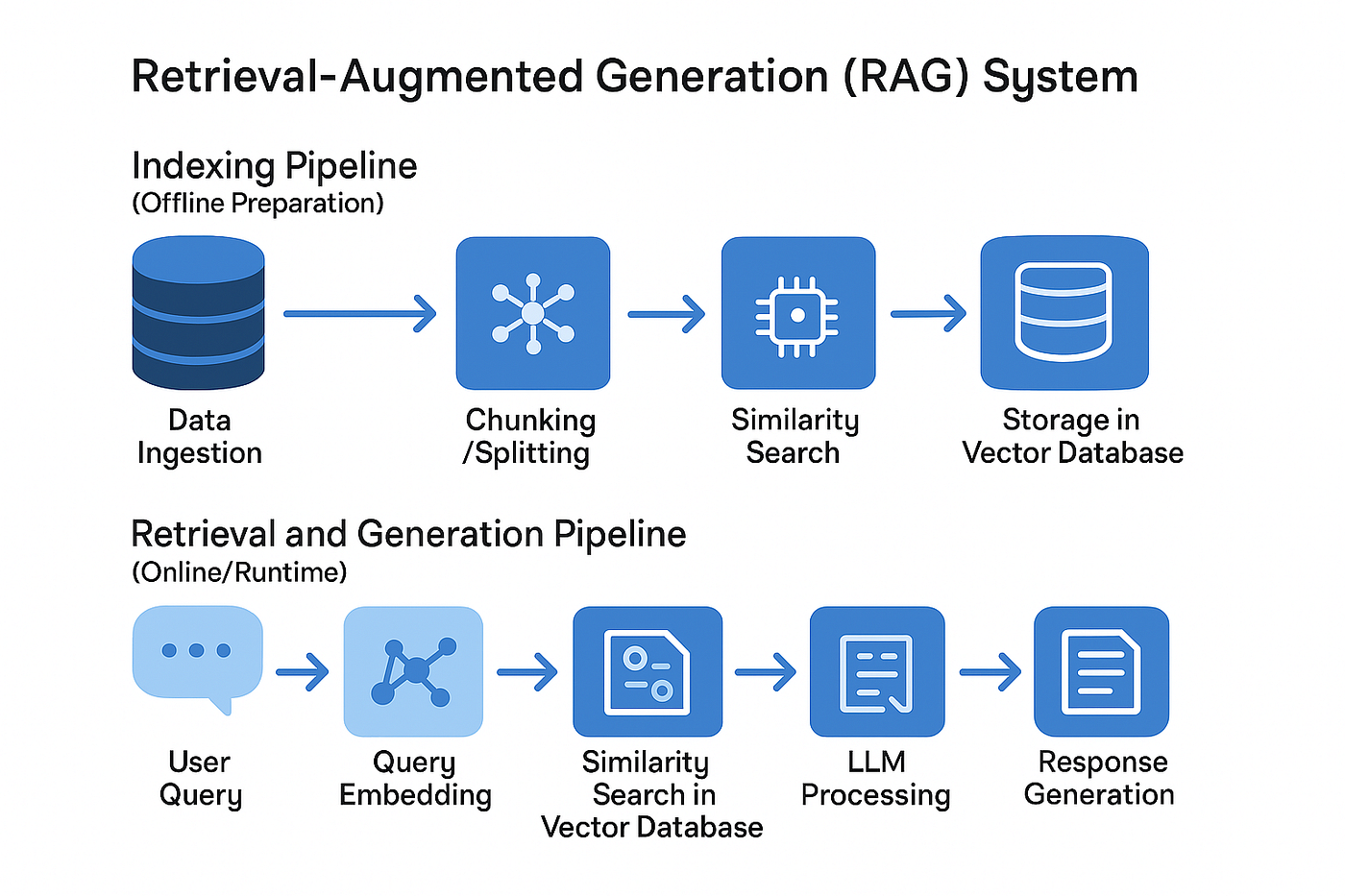
11 — Knowledge Base Integration (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
This is where your chatbot stops being “generic AI” and becomes your bot.
The modern technique:
RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
Process:
-
User asks a question
-
chatbot searches stored knowledge
-
retrieves matching text
-
feeds it into the model
-
model answers using that data only
Example:
User: “What are your business hours?”
Bot retrieves from stored docs:
We are open from 9am–6pm GMT+1, Monday–Friday.
Bot responds with that exact verified info.
12 — Memory System: Giving the Chatbot a “Mind”
We implement:
Short-term memory
Stored in:
-
conversation buffer
Working memory
Stored in:
-
summarized context chunks
Long-term memory
Stored in:
-
vector database (ChromaDB, Pinecone, Qdrant, Weaviate, Redis vector store)
Example behavior for general AI assistant:
User: “My birthday is July 14.”
Later…
Bot: “By the way, your birthday is in 2 months — anything planned?”
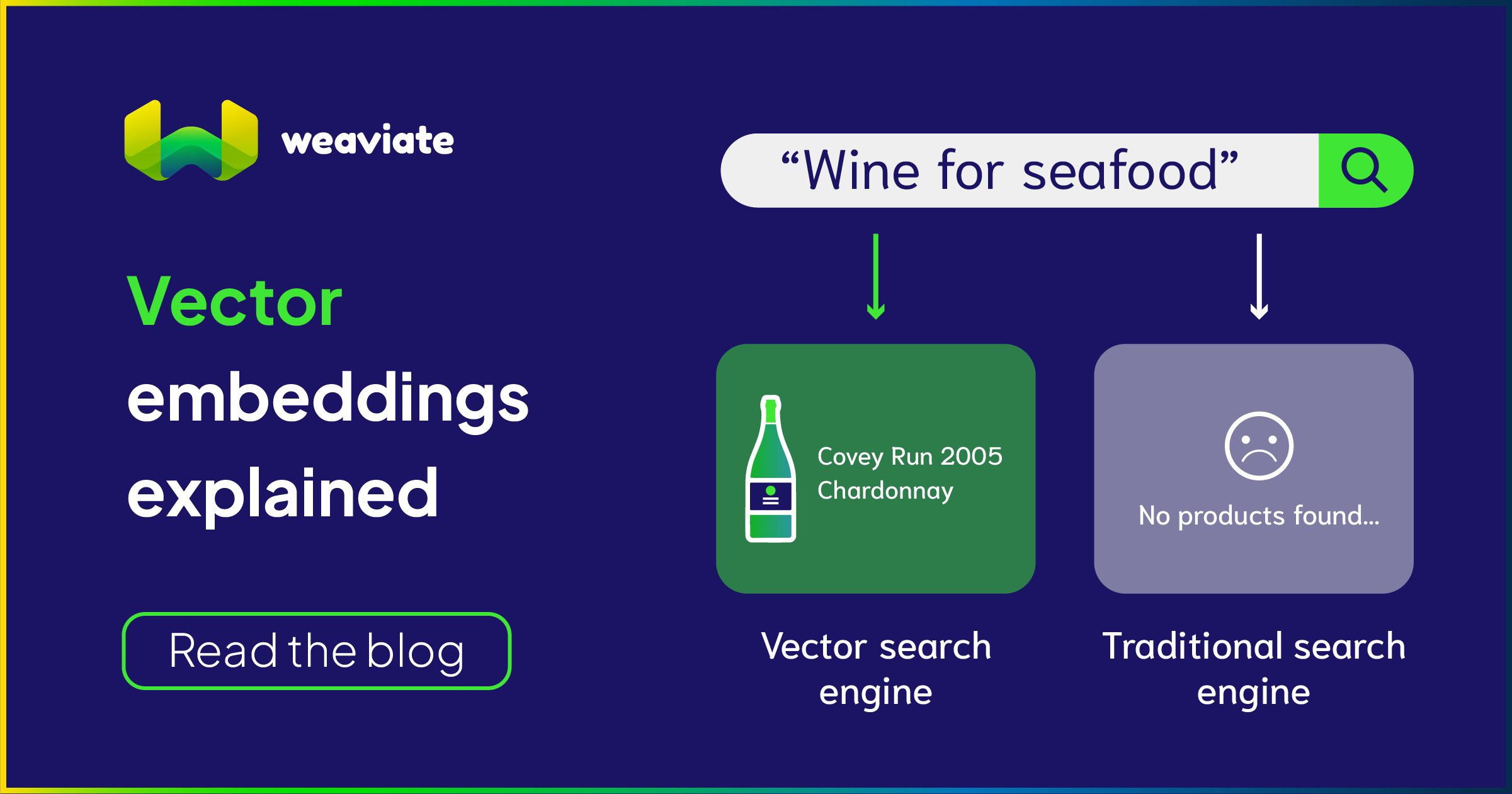
13 — Handling Uncertainty & Avoiding Hallucinations
We add safety fallback techniques:
1. Confidence scoring
If low → respond:
I’m not certain — could you clarify?
2. Answer with sources
When referencing stored knowledge
According to your uploaded document…
3. Ask a follow-up question
Did you mean A or B?
4. Never invent numbers, citations, or facts
This makes your bot reliable.
14 — Front-End Integration (Real Example)
Your AI assistant can exist in:
-
Mobile app
-
WhatsApp
-
Telegram
-
Discord
-
Slack
-
Browser extension
-
API endpoint
-
OS-level assistant
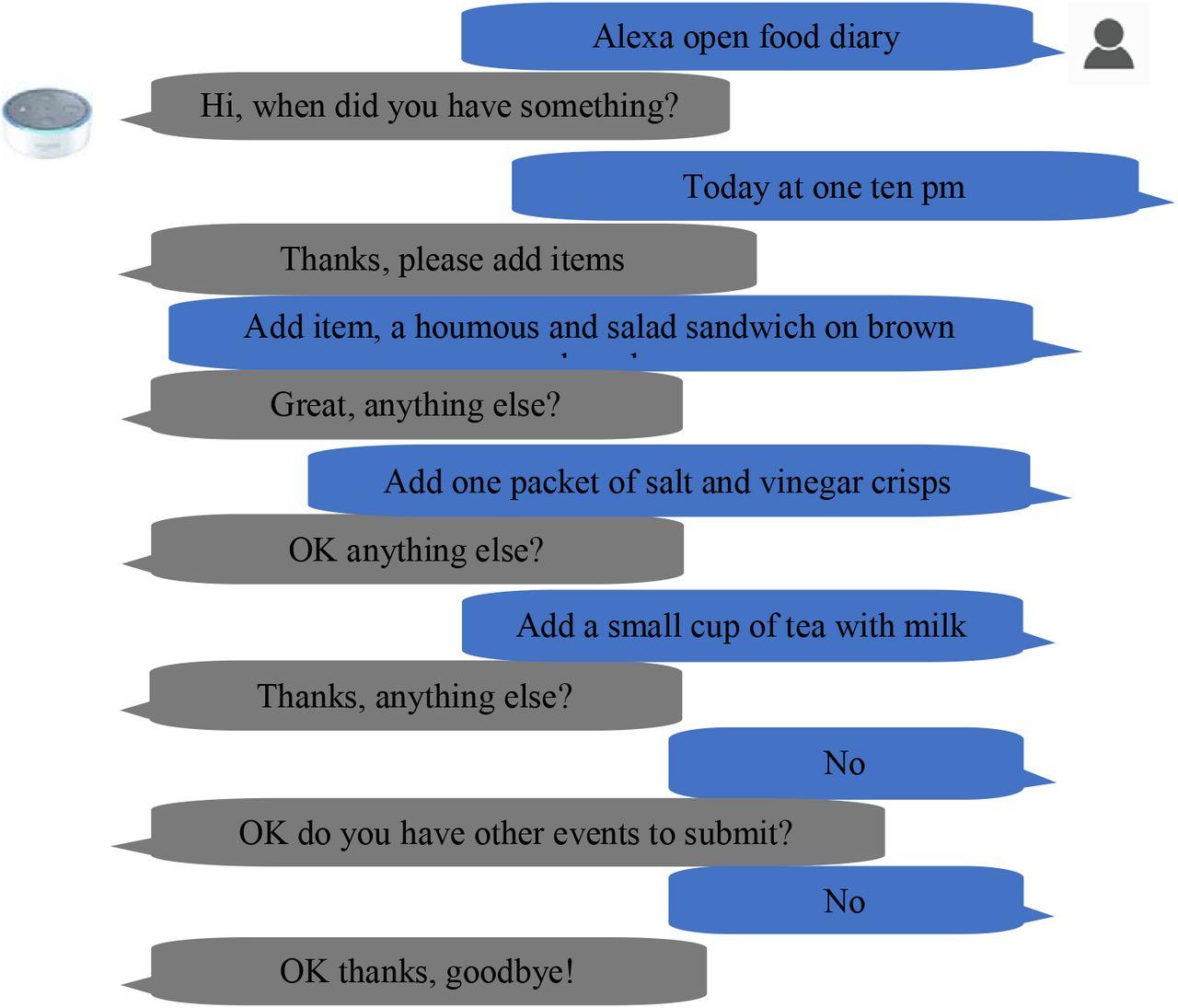
15 — Example Dialogue (Your General AI Assistant in Action)
User: explain blockchain like I’m 10
Bot: Imagine a notebook that everyone can see, and every time something is written in it, everyone gets a copy. Nobody can erase a past entry, so everyone always knows what really happened.
User: summarize this text…
Bot: Sure — here are the 5 key ideas…
User: write me a polite decline message for a job offer
Bot: Certainly — here’s a human-sounding and respectful version…
User: can you remember my writing style?
Bot: Yes — I’ll adapt my tone and word choice to match your style throughout future responses.
16 — Analytics & Optimization (Business Outcome Focus)
A chatbot should improve over time using:
-
unanswered question logs
-
user satisfaction score
-
intent mismatch logs
-
message timing latency
-
session duration
-
conversion metrics
-
retention
This leads to iterative refinement.
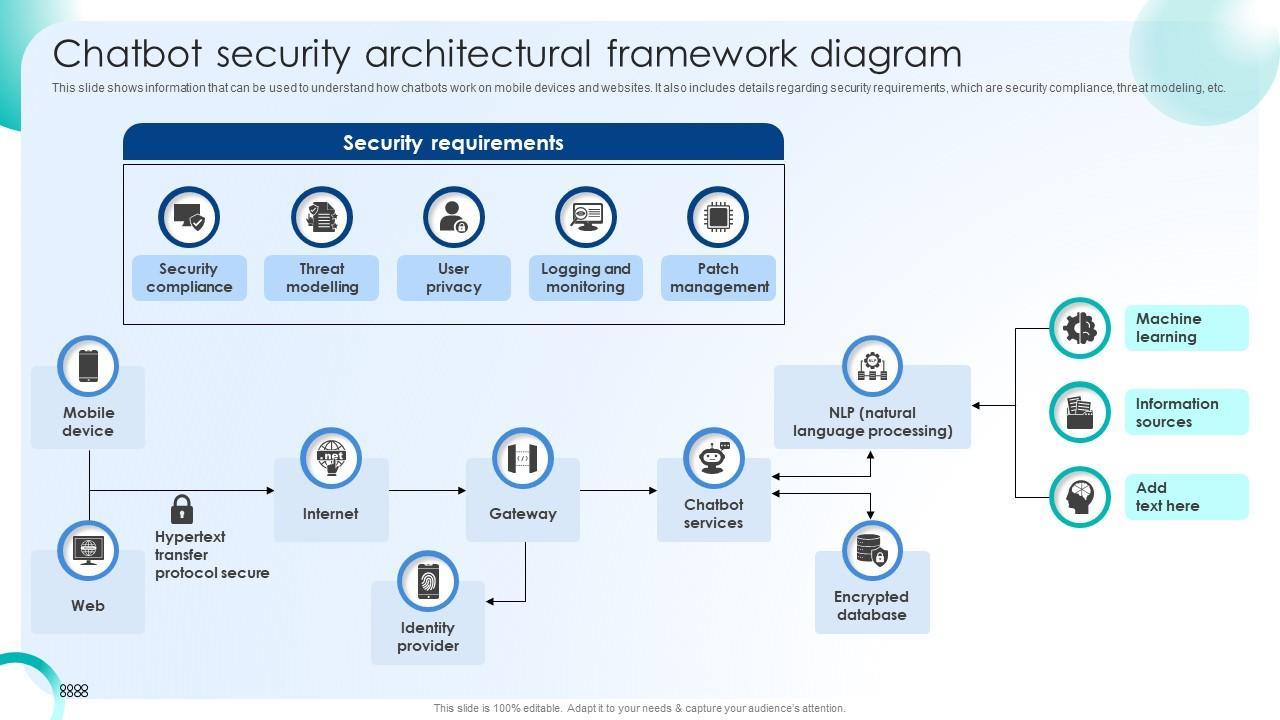
17 — Security, Privacy & Compliance (Critical for Deployment)
A responsible chatbot must ensure:
-
anonymization
-
GDPR compliance
-
response filtering
-
anti-leak behavior
-
rate limiting
18 — Deployment & Scaling
You can deploy on:
-
Google Cloud
-
Azure
-
Docker container
Scaling considerations:
-
handle concurrent users
-
load balancing
-
model quantization
-
GPU utilization
19 — Future of AI Chatbots (2025–2030)
Your general AI assistant will soon be able to:
-
understand voice
-
generate voice replies
-
store lifelong memory
-
behave as a personal digital employee
-
integrate with personal task automation
-
anticipate user needs
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between a chatbot and a conversational AI?
A chatbot typically uses predefined responses or simple keyword matching, while conversational AI uses machine learning and natural language understanding to interpret user intent, maintain context, and generate intelligent, flexible responses.
2. Do I need programming skills to create a chatbot?
No. Many no-code tools allow you to build a chatbot using visual builders and templates. However, if you want a highly customized AI assistant with memory, integrations, and unique capabilities — programming knowledge or a technical team becomes useful.
3. Which programming languages are best for building chatbots?
Popular choices include:
-
Python (most common for AI & NLP)
-
JavaScript / Node.js (great for web integration)
-
TypeScript
-
Go (fast & efficient)
Python dominates in the AI space due to libraries like spaCy, HuggingFace, TensorFlow, and LangChain.
4. Which AI model should I use for my chatbot?
It depends on your needs:
-
For quick setup → GPT-based APIs
-
For enterprise privacy → self-hosted Llama/Mistral
-
For limited hardware → smaller optimized models
The best approach is often hybrid:
Use an external LLM for reasoning + a private local knowledge base for proprietary data.
5. Can a chatbot learn from user interactions over time?
Yes — if designed with memory and feedback loops.
Chatbots can use:
-
vector databases
-
preference storage
-
personalization data
This allows them to adapt, improve, and eventually predict user needs.
6. How secure is an AI chatbot for business use?
Security depends on implementation. A responsible chatbot should use:
-
data encryption
-
authentication
-
rate limiting
-
filtering
-
compliance (GDPR, ISO, etc.)
Enterprises often prefer storing data locally or on private cloud servers.
7. Can a chatbot replace human support staff?
Not completely.
Ideally:
-
the bot handles repetitive questions
-
humans handle complex, emotional, or exceptional cases
The best setup combines both into a seamless system with human handoff.
8. How do I train a chatbot on my own data?
You provide your materials:
-
website pages
-
PDF documents
-
support logs
-
email archives
-
knowledge base exports
These are indexed into embeddings that the chatbot can recall when answering questions.
9. How long does it take to build a good chatbot?
-
With no-code tools: 1–3 days
-
With low-code integrations: 1–2 weeks
-
With custom development: 1–3 months
The timeline depends on:
-
level of complexity
-
size of knowledge base
-
desired intelligence
-
integrations
-
testing & refinement
10. How much does it cost to run an AI chatbot?
Costs vary depending on scale:
-
Light usage: a few dollars per month
-
Moderate business usage: $50–300/month
-
Heavy enterprise usage: $1,000+/month
Self-hosting can reduce API costs but increases hardware and maintenance expenses.
11. Can a chatbot handle multiple languages?
Yes — modern AI models can understand and respond in:
-
English
-
French
-
German
-
Spanish
-
Portuguese
-
Arabic
-
Chinese
-
and many more
Models like GPT and Llama support multilingual conversation by default.
12. How do I measure chatbot performance?
Important metrics include:
-
user satisfaction rating
-
conversation success rate
-
fallback rate
-
average session duration
-
return users
-
conversion rate
-
cost per assisted interaction
Analytics should guide continuous improvement.
13. What's the difference between training and prompting?
-
Training modifies the model itself (requires deep ML knowledge).
-
Prompting controls how the model responds without retraining (much easier).
Most modern chatbots rely on prompting and RAG — not full model retraining.
14. Can I integrate a chatbot with other tools?
Yes — chatbots can connect to:
-
CRM systems
-
databases
-
spreadsheets
-
inventory systems
-
SMS platforms
-
Slack
-
Teams
-
Zapier
-
n8n
-
Make.com
Integration turns the bot into an automation agent.
15. Are chatbots accurate? Do they make mistakes?
Yes, they can make mistakes.
But accuracy improves dramatically when they:
-
use verified knowledge sources
-
ask clarifying questions
-
cite context sources
-
restrict responses to known data
A well-designed bot can achieve 95–99% accuracy for domain questions.
CONCLUSION
You now have a complete blueprint for building a general-purpose AI assistant that functions:
✔ conversationally
✔ contextually
✔ intelligently
✔ practically
✔ responsibly
Building a powerful AI chatbot requires careful planning, the right tools, and a clear understanding of user needs. Whether you’re a developer or a business owner, this guide provides everything you need to create an intelligent, reliable, and human-like AI assistant. Start building your chatbot today and transform the way you interact with users, automate tasks, and deliver exceptional digital experiences.





